- 4.Knowledge Graph Enhanced Community Detection and Characterization (WSDM 2019 B类)
- Shreyansh Bhatt, Swati Padhee, Amit Sheth, Keke Chen ,Valerie Shalin, Derek Doran, and Brandon Minnery
- [Paper]
- [Java Reference]
Recent studies show that by combining network topology and node attributes, we can better understand community structures in complex networks. However, existing algorithms do not explore “contextually” similar node attribute values, and therefore may miss communities defined with abstract concepts. We propose a community detection and characterization algorithm that incorporates the contextual information of node attributes described by multiple domain-specific hierarchical concept graphs. The core problem is to find the context that can best summarize the nodes in communities, while also discovering communities aligned with the context summarizing communities. We formulate the two intertwined problems, optimal community-context computation, and community discovery, with a coordinate-ascent based algorithm that iteratively updates the nodes’ community label assignment with a community-context and computes the best context summarizing nodes of each community. Our unique contributions include (1) a composite metric on Informativeness and Purity criteria in searching for the best context summarizing nodes of a community; (2) a node similarity measure that incorporates the context-level similarity on multiple node attributes; and (3) an integrated algorithm that drives community structure discovery by appropriately weighing edges. Experimental results on public datasets show nearly 20 percent improvement on F-measure and Jaccard for discovering underlying community structure over the current state-of-the-art of community detection methods. Community structure characterization was also accurate to find appropriate community types for four datasets.
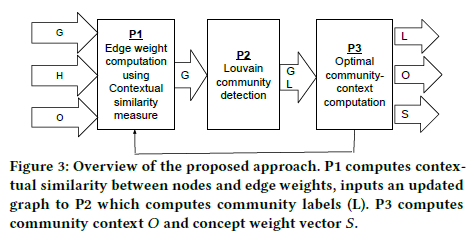
找到描述社区中节点的context,匹配context相符的社区–> optimal community-context computation and community discovery
属性是基于语义的
- 7.Adaptive Community Detection Incorporating Topology and Content in Social Networks (Knowledge-Based Systems 2018 二区)
- Qin Meng, Jin Di, Lei Kai, Bogdan Gabrys, Katarzyna, Musial-Gabrys
- [Paper]
- [Matlab Reference]
In social network analysis, community detection is a basic step to understand the structure and function of networks. Some conventional community detection methods may have limited performance because they merely focus on the networks’ topological structure. Besides topology, content information is another significant aspect of social networks. Although some state-of-the-art methods started to combine these two aspects of information for the sake of the improvement of community partitioning, they often assume that topology and content carry similar information. In fact, for some examples of social networks, the hidden characteristics of content may unexpectedly mismatch with topology. To better cope with such situations, we introduce a novel community detection method under the framework of non-negative matrix factorization (NMF). Our proposed method integrates topology as well as content of networks and has an adaptive parameter (with two variations) to effectively control the contribution of content with respect to the identified mismatch degree. Based on the disjoint community partition result, we also introduce an additional overlapping community discovery algorithm, so that our new method can meet the application requirements of both disjoint and overlapping community detection. The case study using real social networks shows that our new method can simultaneously obtain the community structures and their corresponding semantic description, which is helpful to understand the semantics of communities. Related performance evaluations on both artificial and real networks further indicate that our method outperforms some state-of-the-art methods while exhibiting more robust behavior when the mismatch between topology and content is observed.
属性是基于关键词的 0-1 矩阵
- 9.Discovering Fuzzy Structural Patterns for Graph Analytics (IEEE TFS 2018 一区)
- Tiantian He and Keith C. C. Chan
- [Paper]
- [Executable Reference]
Many real-world datasets can be represented as attributed graphs that contain vertices, each of which is associated with a set of attribute values. Discovering clusters, or communities, which are structural patterns in these graphs, are one of the most important tasks in graph analysis. To perform the task, a number of algorithms have been proposed. Some of them detect clusters of particular topological properties, whereas some others discover them mainly based on attribute information. Also, most of the algorithms discover disjoint clusters only. As a result, they may not be able to detect more meaningful clusters hidden in the attributed graph. To do so more effectively, we propose an algorithm, called FSPGA, to discover fuzzy structural patterns for graph analytics. FSPGA performs the task of cluster discovery as a fuzzy-constrained optimization problem, which takes into consideration both the graph topology and attribute values. FSPGA has been tested with both synthetic and real-world graph datasets and is found to be efficient and effective at detecting clusters in attributed graphs. FSPGA is a promising fuzzy algorithm for structural pattern detection in attributed graphs.
一个属性相似性的矩阵表示两个节点属性的相似程度
-20.A Unified Semi-Supervised Community Detection Framework Using Latent Space Graph Regularization (IEEE TOC 2015 A类)
- Liang Yang, Xiaochun Cao, Di Jin, Xiao Wang, and Dan Meng
- [Paper]
- [Matlab Reference]
Community structure is one of the most important properties of complex networks and is a foundational concept in exploring and understanding networks. In real world, topology information alone is often inadequate to accurately find community structure due to its sparsity and noises. However, potential useful prior information can be obtained from domain knowledge in many applications. Thus, how to improve the community detection performance by combining network topology with prior information becomes an interesting and challenging problem. Previous efforts on utilizing such priors are either dedicated or insufficient. In this paper, we firstly present a unified interpretation to a group of existing community detection methods. And then based on this interpretation, we propose a unified semi-supervised framework to integrate network topology with prior information for community detection. If the prior information indicates that some nodes belong to the same community, we encode it by adding a graph regularization term to penalize the latent space dissimilarity of these nodes. This framework can be applied to many widely-used matrix-based community detection methods satisfying our interpretation, such as nonnegative matrix factorization, spectral clustering, and their variants. Extensive experiments on both synthetic and real networks show that the proposed framework significantly improves the accuracy of community detection, especially on networks with unclear structures.
pairwise prior information 提前知道两个节点属于同一个社区,提供了一个多种属性相似性衡量的接口
- 21.Community Detection Based on Structure and Content: A Content Propagation Perspective (ICDM 2015 B类)
- Liyuan Liu, Linli Xu, Zhen Wang, and Enhong Chen
- [Paper]
- [Matlab Reference]
用f表示feature vector,可以是value
- 22.Nonnegative Matrix Tri-Factorization with Graph Regularization for Community Detection in Social Networks (IJCAI 2015 A类)
- Mark Kozdoba and Shie Mannor
- [Paper]
- [Python Reference]
Community detection on social media is a classic and challenging task. In this paper, we study the problem of detecting communities by combining social relations and user generated content in social networks. We propose a nonnegative matrix tri-factorization (NMTF) based clustering framework with three types of graph regularization. The NMTF based clustering framework can combine the relations and content seamlessly and the graph regularization can capture user similarity, message similarity and user interaction explicitly. In order to design regularization components, we further exploit user similarity and message similarity in social networks. A unified optimization problem is proposed by integrating the NMTF framework and the graph regularization. Then we derive an iterative learning algorithm for this optimization problem. Extensive experiments are conducted on three real-world data sets and the experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
属性是基于twitter message的word
- 23.Community Detection in Networks with Node Attributes (ICDM 2013 B类)
- Jaewon Yang, Julian McAuley, and Jure Leskovec
- [Paper]
- [C++ Reference]
binary-valued attributes
- 24.A Model-based Approach to Attributed Graph Clustering (SIGMOID 2012 A类)
- Zhiqiang Xu, Yiping Ke, Yi Wang, Hong Cheng, and James Cheng
- [Paper]
- [Matlab Reference]
Graph clustering, also known as community detection, is a longstanding problem in data mining. However, with the proliferation of rich attribute information available for objects in real-world graphs, how to leverage structural and attribute information for clustering attributed graphs becomes a new challenge. Most existing works take a distance-based approach. They proposed various distance measures to combine structural and attribute information. In this paper, we consider an alternative view and propose a model-based approach to attributed graph clustering. We develop a Bayesian probabilistic model for attributed graphs. The model provides a principled and natural framework for capturing both structural and attribute aspects of a graph, while avoiding the artificial design of a distance measure. Clustering with the proposed model can be transformed into a probabilistic inference problem, for which we devise an efficient variational algorithm. Experimental results on large real-world datasets demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms the state-of-art distance-based attributed graph clustering method
value matrix
- 25.Graph Clustering Based on Structural/Attribute Similarities (WSDM 2009 B类)
- Yang Zhou, Hong Cheng, Jeffrey Xu Yu
- [Paper]
- [Python Reference]
相同的属性成为一个属性节点作为结构性质
Abstract
The goal of graph clustering is to partition vertices in a large graph into different clusters based on various criteria such as vertex connectivity or neighborhood similarity. Graph clustering techniques are very useful for detecting densely connected groups in a large graph. Many existing graph clustering methods mainly focus on the topological structure for clustering, but largely ignore the vertex properties which are often heterogenous. In this paper, we propose a novel graph clustering algorithm, SA-Cluster, based on both structural and attribute similarities through a unified distance measure. Our method partitions a large graph associated with attributes into k clusters so that each cluster contains a densely connected subgraph with homogeneous attribute values. An effective method is proposed to automatically learn the degree of contributions of structural similarity and attribute similarity. Theoretical analysis is provided to show that SA-Cluster is converging. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of SA-Cluster through comparison with the state-of-the-art graph clustering and summarization methods.
graph clustering measures vertex closeness based on connectivity (e.g., the number of possible paths between two vertices) and structural similarity (e.g., the number of common neighbors of two vertices);
while relational data clustering measures distance mainly based on attribute similarity (e.g.Euclidian distance between two attribute vectors).

The goal is to partition the graph into k clusters with cohesive intra-cluster structures and homogeneous attribute values. The problem is quite challenging because structural and attribute similarities are two seemingly independent, or even conflicting goals